Federation of South Arabia
Federation of South Arabia اتحاد الجنوب العربي Ittiḥād al-Janūb al-‘Arabī | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1962–1967 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Status | British protectorate | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Aden | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic English South Arabian | ||||||||||||
| Government | Federal monarchy | ||||||||||||
| High Commissioner | |||||||||||||
• 1963 | Sir Charles Johnston | ||||||||||||
• 1963–1964 | Sir Kennedy Trevaskis | ||||||||||||
• 1964–1967 | Sir Richard Turnbull | ||||||||||||
• 1967 | Sir Humphrey Trevelyan | ||||||||||||
| Chief Minister | |||||||||||||
• 1963 | Hassan Ali Bayumi | ||||||||||||
• 1963–1965 | Zayn Abdu Baharun | ||||||||||||
• 1965 | Abdul-Qawi Hassan Makkawi | ||||||||||||
• 1965–1966 | Ali Musa al-Babakr | ||||||||||||
• 1966–1967 | Salih al-Awadli | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||
• Established | 4 April 1962 | ||||||||||||
• Independence | 30 November 1967 | ||||||||||||
| Currency | South Arabian dinar | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
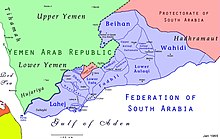

The Federation of South Arabia (FSA; Arabic: اتحاد الجنوب العربي Ittiḥād al-Janūb al-‘Arabī) was a federal state under British protection in what would become South Yemen. Its capital was Aden.[1]
History
[edit]Originally formed on April 4, 1962 from 15 states of the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South. On January 18, 1963, the Royal Colony of Aden joined it. After the annexation of the Upper Aulaki Sultanate in June 1964, the federation included 17 states.
On July 23, 1962, negotiations began in London between the British Minister of Colonies, Duncan Sandys, and the ministers of the Federation of South Arabia and the Colony of Aden. The parties raised the issue of the constitutional status of Aden and the conditions for its entry into the federation. Numerous parties and organizations in Aden protested against these negotiations, declaring that the colonial ministers did not have the right to decide the fate of the population of Aden and that only the national government of Aden, created by general elections, would be competent to decide the question of a union with the federation. To achieve all this, it was necessary to eliminate its dependence on England. Representatives of the opposition, led by the Aden Trade Union Congress, said that any union concluded against the will of the people of Aden would be dissolved at the first opportunity. On the day the London negotiations began, a protest strike was declared in Aden. The Aden Trade Union Congress called for this strike, despite the fact that Aden had had a law prohibiting strikes since 1960, and violators were subject to imprisonment.[2][3]
On August 16, 1962, negotiations ended with the signing of an agreement, according to which Aden, while remaining under British sovereignty, was to become part of the Federation of South Arabia on March 1, 1963. The agreement provided that the federation agreement, signed on February 11, 1959, will remain in force, and the new agreement will be only an addition to it.[4] During these negotiations, agreement was also reached to introduce minor changes to the constitutional status of Aden once it became part of the federation.[5]
In 1965, the British temporarily removed the government of the Federation of South Arabia and imposed direct colonial rule.[6]
In 1966, the federation team took part in the Commonwealth Games in Kingston, Jamaica. The Federation was dissolved following independence along with the Protectorate of South Arabia and the formation of the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen on November 30, 1967.
States
[edit]| Flag | Name | Established | Joined | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
State of Aden | 1963 | ||
 |
Alawi Sheikhdom | unknown | ||
 |
Aqrabi Sheikhdom | 1770 | ||

|
Audhali Sultanate | 18th century | ||

|
Emirate of Beihan | 1680 | ||

|
Dathina Sheikhdom | 18th century | ||

|
Emirate of Dhala | early 19th century | ||

|
Fadhli Sultanate | 17th century | ||

|
Haushabi Sultanate | 18th century | ||

|
Sultanate of Lahej | 1728 | 1872 | formerly ruled over Aden |
 |
Lower Aulaqi Sultanate | 18th century | ||

|
Sultanate of Lower Yafa | ca. 1800 | ||

|
Muflahi Sheikhdom | 1850 | ||

|
Sheikhdom of Shaib | 18th century | ||

|
Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom | 18th century | ||

|
Upper Aulaqi Sultanate | 18th century | ||

|
Wahidi Sultanate | 1830 | consisted originally of four sub-sultanates: Wahidi Balhaf, Wahidi Azzan, Wahidi Bir Ali, Wahidi Haban |
List of rulers
[edit]| State | Last Ruler | Deposed | House | Reign | Ref(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salih ibn Sayil | 28 August 1967 | Al Alawi | Last reigning Sheikh (1940–1967). | [7] | |
| Mahmud ibn Muhammad | 28 August 1967 | Al Aqrabi | Last reigning Sheikh (1957–1967). | [7] | |
| Salih ibn al-Husayn | 17 September 1967 | Al Audhali | Last reigning Sultan (1928–1967). | [7] | |
| Nasir ibn Aidrus | 29 November 1967 | Al Awlaqi | Last reigning Sultan (1947–1967). | [7] | |
| Awad ibn Salih | 29 November 1967 | Al Awlaqi | Last reigning Sultan (1935–1967). | [7] | |
| Saleh bin al-Husayn | 28 August 1967 | Al Habieli | Last reigning Emir (1935–1967). | [7] | |
| Shafaul ibn Ali Shaif | 17 August 1967 | Al Amiri | Last reigning Emir (1954–1967). | [7] | |
| Nasir bin Abdullah | 29 November 1967 | Al Fadhli | Last reigning Sultan (1964–1967). | [7] | |
| Faisal bin Surur | 29 November 1967 | Al Haushabi | Last reigning Sultan (1955–1967). | [7] | |
| Fadhl VI bin Ali | 17 August 1967 [as 1] | Al Abdali | Last reigning Sultan (1958–1967). | [7] | |
| Ali ibn Muhammad | 17 August 1967[as 3] | Al Wahidi | Last governing Hakim (1967). | [7] | |
| Alawi ibn Salih | 29 November 1967[as 4] | Last reigning Sultan (1955–1967). | [7] | ||
| Husayn ibn Abdullah | 29 November 1967[as 5] | Last reigning Sultan (until 1967). | [7] | ||
| Mahmud ibn Aidrus | 28 August 1967[as 6] | Al Afifi[as 7] | Last reigning Sultan (1954–1967). | [7] |
- ^ Prior to his formal ascension to the throne, he had served as prince regent since 10 July 1958.[7]
- ^ Known as Balhaf and Azzan from 1881, signifying Balhaf's merge with Wahidi Azzan. Known simply as Wahidi from 1962, when the sultanates of Wahidi Bir Ali and Wahidi Haban were made subordinate.[7]
- ^ Prince Ali held the position of hakim (regent) from 20 February 1967 until the sultanate's abolition in August of the same year. He was never crowned sultan.[7]
- ^ Alawi previously reigned as sultan from 1955 until the monarchy was abolished in 1967. Before his reign ended, he was made subordinate to the Sultan of Balhaf and Azzan on 23 October 1962.[7]
- ^ Husayn had previously reigned as sultan prior to the monarchy's abolition in 1967. Before his reign ended, he was made subordinate to the Sultan of Balhaf and Azzan on 23 October 1962.[7]
- ^ Mahmud previously reigned as sultan from 1954 until the monarchy was deposed in 1967. His reign was not initially recognised by the British government, which continued to recognise his still-living father and predecessor as sultan until 1958.[7]
- ^ A clan of the Yafa tribe. The Yafai are divided into ten sheikhdoms that were spread across the former sultanates of Lower Yafa and Upper Yafa.[8]
Chief Ministers
[edit]- Hassan Ali Bayumi (18 January 1963 – 24 June 1963)
- Zayn Abdu Baharun (9 July 1963 – 23 January 1965)
- Abdul-Qawi Hassan Makkawi (7 March 1965 – 25 September 1965)
- Ali Musa al-Babakr (25 September 1965 – 30 August 1966)
- Salih al-Awadli (30 August 1966 – 30 November 1967)
High Commissioners
[edit]- Sir Charles Johnston (18 January 1963 – 17 July 1963)
- Sir Kennedy Trevaskis (17 July 1963 – 21 December 1964)
- Sir Richard Turnbull (21 December 1964 – 22 May 1967)
- Sir Humphrey Trevelyan (22 May 1967 – 30 November 1967)
Postage stamps
[edit]
The Federation issued its own Adeni postage stamps from 1963 to 1966. Most of its issues were part of the omnibus issues common to all the Commonwealth territories, but it did issue its own definitive stamps on 1 April 1965. The set of 14 included 10 values, from 5 to 75 fils, each depicting the arms of the Federation in a single color, while the top four values (100 fils, 250 fils, 500 fils, and 1 dinar), featured the flag of the Federation.
The stamps referred to above are those listed in the Scott Standard Postage Stamp Catalog. A number of other stamps have also been issued and are listed in Stanley Gibbons and other widely used stamp catalogs. It is possible, or even likely, that some of the stamps of South Arabia were not issued primarily for postal use.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Parliament Building in Al Ittihad, the capital of the Federation of South Arabia
- ^ «The Times» (24.VII.1962), p. 8.
- ^ «Aden Chronicle» (July 12, 1962), p. 1.
- ^ «Aden Chronicle» (August 23, 1962), p. 3.
- ^ «Aden Chronicle» (October 4, 1962), pp. 1, 28.
- ^ Dean, Lucy (2004). "The Middle East and North Africa". Издание 2004 года. Routledge. Страница 1211. ISBN 978-1-85743-184-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Cahoon, Ben. "States of the Aden Protectorates". World Statesmen.org. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ^ A Collection of First World War Military Handbooks of Arabia, 1913–1917. Vol. 3. Archive Editions. 1988. pp. 84–93. ISBN 978-1-85207-086-1.
Further reading
[edit]- Paul Dresch. A History of Modern Yemen. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
- R.J. Gavin. Aden Under British Rule: 1839-1967. London: C. Hurst & Company, 1975.
- Tom Little. South Arabia: Arena of Conflict. London: Pall Mall Press, 1968.
External links
[edit] Media related to Federation of South Arabia at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Federation of South Arabia at Wikimedia Commons- South Arabia and Yemen, 1945-1995


