Tararua Range
| Tararua Range | |
|---|---|
 Tararua Range from Wairarapa | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Pukeamoamo / Mitre |
| Elevation | 1,570 m (5,150 ft) |
| Geography | |
| Country | New Zealand |
| Region | Wellington |
| Range coordinates | 40°48′S 175°24′E / 40.8°S 175.4°E |
| Borders on | Remutaka Range and Ruahine Range |


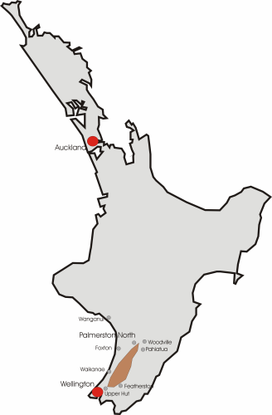
The Tararua Range, often referred to as the Tararua Ranges or Tararua, is one of several mountain ranges in the North Island of New Zealand.
The Tararua Range runs northeast–southwest for 80 km (50 mi) from near Palmerston North to the upper reaches of the Hutt Valley, where the northern tip of the Remutaka Range begins. It is separated in the north from the southern end of the Ruahine Range by the Manawatū Gorge.[1] Most of the Range is wilderness, protected as the Tararua Forest Park.
The highest peak in the Tararua Range is Pukeamoamo / Mitre (not to be confused with Mitre Peak) at 1,570 m (5,150 ft). Other prominent peaks include Mount Bannister at 1,537 m (5,043 ft) and Mount Hector at 1,529 m (5,016 ft), which is named after the scientist Sir James Hector. Its Māori name is Pukemoumou, or 'hill of desolation'.[1]
Geography
[edit]The Tararua Range is divided into two distinct northern and southern regions. Each of these is dominated by a central mountain peak: Arete in the north and Hector in the south. A total of ten rivers rise on the mountain slopes, providing water for the surrounding rural and urban areas from Palmerston North to Wellington. A number of ranges radiate out from the mountains, the largest of which is the Main Range linking the twin clusters of northern and southern peaks.[2] The summits of the ranges average between 1,300 and 1,500 metres in height. This consistency indicates that the region was once part of a level plain. About 10 million years ago parts of this relatively low-lying area were thrust up, creating a mountainous backbone for the southern part of the North Island. Subsequent erosion contributed to the present pattern of parallel ranges divided by deep river valleys. The ranges provide a back-drop for the Kāpiti coastal plain.[3]
Mountain peaks
[edit]The 15 peaks in the Tararua Range of 1,500 m or higher are (from north to south):
| Name | Elevation |
|---|---|
| Logan | 1,500 m |
| Bannister | 1,537 m |
| South Bannister | 1,513 m |
| Arete | 1,505 m |
| Lancaster | 1,504 m |
| Brocket | 1,538 m |
| Pukeamoamo / Mitre | 1,571 m |
| Peggys Peak | 1,545 m |
| Girdlestone | 1,546 m |
| North King | 1,535 m |
| Middle King | 1,521 m |
| South King | 1,531 m |
| McGregor | 1,540 m |
| Angle Knob | 1,510 m |
| Mount Hector | 1,529 m |
Other notable peaks in the range are Jumbo Peak (1,405 m) and Mount Holdsworth (1,470 m).
Climate and vegetation
[edit]The western slopes of the ranges are subject to prevailing moisture-carrying winds, channelled by Cook Strait to the south. These are the source of an annual rainfall of approximately 5,000 mm, resulting in the dominance of conifers, ferns and shrubs on the western side of the ranges. By contrast, the pattern on the eastern side is one of open beech forest in a drier environment.[1] In spite of a reputation of being composed of gloomy bush, impenetrable leatherwood, and wet snow tussocks on mist-shrouded tops, the Tararua Range has a wide diversity of vegetation, ranging from alpine tussock grasslands and subalpine shrublands to forests of montane miro/kamahi, or beech or lowland broadleaf forests with emergent podocarps and kamahi.[4]
The forest in the northern part of the Tararua Range consists mainly of tawa and miro indigenous woodlands. Further south species such as beech are widely seen. Finally, along the west slopes of the ranges facing the Tasman Sea, mixed native species such as rimu, tarrier, mataī, tōtara and kahikatea are dominant.[5]
History
[edit]The rugged terrain and frequently harsh weather of the Tararua Range served to discourage any substantial attempt at penetration by early Māori. Although there is archaeological evidence of exploration by moa hunters as early as the twelfth century, the mountains remained a massive physical divide between the tribal settlements located along rivers, lakes and coastlines to the east and west. Some of the Kāti Māmoe (early Māori settlers on the neighbouring Kāpiti Coast) are reputed to have taken refuge in the Tararua mountains after they were displaced by the Rangitane and Muaūpoko iwi (tribal groups). The Kāti Māmoe survivors attained a mythical status as the patupaiarehe (fairy folk) of the Tarurua Range.[6] In the 1820s the Muaūpoko in turn were forced to flee to the ranges when under attack by the Ngāti Toa led by Te Rauparaha. In spite of such intrusions, the mountain range remained the home of distant gods or hostile wild men (maero). As such, it was a special place to be respected but avoided.[7]
In the 1870s a large portion of the ranges was sold to the New Zealand Government by a coalition of the Iwi in possession of the surrounding region. Specifically excluded from this "Tararua Block" purchase was an area of 1,000 acres reserved to protect the sacred lake Hapuakorari, the exact location of which remained uncertain.[8] European settlers, like their Māori counterparts, found the steep ridges and deep valleys of the Tararua Range difficult of access and intimidating in scale. The range accordingly escaped the development of the fertile plains that bordered on it. In 1881 36,000 acres of the Tararua Block, including key catchment areas for four rivers, was classified as State Forest, subject to protection. Additional watersheds were added over the following decades, to create a Crown conservation reserve in excess of 250,000 acres. The scenic beauty of the Tararua Range made the mountains a popular subject for paintings during the Victorian period – though largely romanticized and usually undertaken from a distance.[9] By the 1920s, with the neighbouring countryside largely settled, the potential of the range as an area for outdoor recreation rather than for exploitation began to be recognised.[10]
Tararua Forest Park
[edit]
The 116,535 hectare Tararua Forest Park covers more than three-quarters of the Tararua Range. It is administered by the New Zealand Department of Conservation and extends from the Pahiatua Track in the north, to the Rimutaka Saddle in the south. The main entrance on the eastern side of the ranges is at Holdsworth, and on the west side from Ōtaki Forks.
Roads
[edit]The only all-weather road right across the range is the Pahiatua Track, which joins Palmerston North and Pahiatua. It is now used more heavily since the Manawatū Gorge road was permanently closed in 2017 due to recurring large landslides.[citation needed]
Recreation
[edit]The Tararua Range serves as a popular tramping location for the greater Wellington district. It is one of the most frequently entered ranges in the country, with between 120,000 and 150,000 people visiting each year. Among the many tramping tracks is the well-known Southern Crossing running from Ōtaki Forks in the west, over Mount Hector and exiting via Kaitoke.[1]
Camping
[edit]
The hills include 6 campsites.[11] They are accessible by car, although visitors may need to travel over gravel roads that contain occasional fords. Campsites are generally located within the foothills of the range, alongside a river or stream.
Tramping
[edit]
The Tararua Range is significant in the history of tramping in New Zealand, due to its accessibility for people in Wellington and nearby towns. Two of the most popular tracks are the Northern Crossing from Levin to the Wairarapa, and the Southern Crossing from Ōtaki Forks to near Masterton.
The Sutch Search
[edit]In April 1933, the Tararua Range was the focus of what later came to be known as The Sutch Search when Mr. Eric Hill, Miss Morva Williams, Mr. Bert O’Keefe and Dr. Bill Sutch went missing for more than two weeks during an attempt to traverse from Te Matawai Hut to Mount Holdsworth during winter. An accident while sidling the Broken Axe Pinnacles prevented the group getting to Mt Holdsworth in a day as planned. Then bad weather forced them off the ridge tops. It took more than two weeks for them to find a route down the untracked Waiohine River.[12] The group was noticed to be missing after a week, at which time a search developed that eventually involved roughly 200 people and solicited many donations from members of the public. The search was the first in New Zealand to involve radio communications and aircraft, and is generally considered to be one of the major contributing events towards the formation of New Zealand's voluntary Land Search and Rescue service (LSAR).[13] It was covered intensely by media at the time, and when the group finally returned they sparked strong public debate regarding the responsibilities of those who enter the wilderness.[14]
Tramping fatalities
[edit]A combination of steep terrain, dense bush, difficult river crossings and changeable winter weather conditions has caused over twenty-two tramping deaths in the Tararua Range since 1970, most recently one in January 2023.[15]
Other deaths included those of the Chief Executive of the National Museum of New Zealand Te Papa: Dr Seddon Bennington and a friend Marcella Jackson, who died of hypothermia in June 2009.[16][10]
Mountain running racing
[edit]The Tararua Mountain Race, following a track of 35.4 km (22.0 mi), from Kaitoke to Ōtaki Forks, has been held annually since 1990. The running race involves a total ascent of 2,250 m (7,380 ft) plus a slightly longer descent, and requires the deployment of 50 volunteers as marshals, search and rescue teams, first aid helpers, and support staff.[17] It frequently encounters adverse weather and is not regarded as a suitable event for inexperienced participants.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Maclean, Chris (3 March 2011). "Wellington places – Tararua Range". Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ^ Maclean (1994), pp. 26–30
- ^ McKenzie, D. W. New Zealand Atlas. p. 48. ISBN 0-86863-466-2.
- ^ "Vegetation in Tararua Forest Park". Department of Conservation. 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2012.
If you think the vegetation of the Tararua Range is just gloomy bush, impenetrable leatherwood, and wet snow tussocks on the mist-shrouded tops you will be pleasantly surprised if you look closer.
- ^ McKenzie, D. W. New Zealand Atlas. p. 815. ISBN 0-86863-466-2.
- ^ Maclean (1994), page 41
- ^ Maclean (1994), pages 68 and 78
- ^ Maclean (1994), pp. 68–71
- ^ Maclean (1994), pp. 106–107
- ^ a b Macdonald, Nikki (26 October 2010). "Lost: How tramp turned to tragedy". Dominion Post. Retrieved 8 October 2019.
- ^ Department of Conservation. "Tararua Forest Park". Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ Maclean (1994)
- ^ "History of LandSAR in New Zealand". New Zealand Land Search and Rescue. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ Mike McGavin (27 August 2010). "Re-living the Sutch Search". Windy Hilltops. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ Schwanecke, Gianina (13 January 2023). "Family farewell tramper who died in Tararua Range". Stuff. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ Dominion Post, 15 July 2009
- ^ http://www.tararua-race.org.nz Archived 2013-05-04 at the Wayback Machine
Sources
[edit]Maclean, Chris (December 1994). Tararua: The Story of a Mountain Range. Whitcombe Press. ISBN 978-0-473-02613-4. Retrieved 8 October 2019.
External links
[edit]- Tararua history Department of Conservation
- Tararua Northern Crossing Department of Conservation
- Tararua Southern Crossing Department of Conservation