Lunar Orbiter 1
 Replica of a Lunar Orbiter spacecraft | |||||||||||
| Mission type | Lunar orbiter | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator | NASA | ||||||||||
| COSPAR ID | 1966-073A | ||||||||||
| SATCAT no. | 2394 | ||||||||||
| Website | science.nasa.gov | ||||||||||
| Mission duration | 2 months, 19 days | ||||||||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||||||||
| Manufacturer | Boeing | ||||||||||
| Launch mass | 386.9 kg (853 lb)[1] | ||||||||||
| Dimensions | 3.72 × 1.65 × 1.5 m (12.2 × 5.4 × 4.9 ft)[2] | ||||||||||
| Power | 375 watts[2] | ||||||||||
| Start of mission | |||||||||||
| Launch date | August 10, 1966, 19:31 UTC[3] | ||||||||||
| Rocket | Atlas SLV-3 Agena-D | ||||||||||
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral LC-13 | ||||||||||
| End of mission | |||||||||||
| Disposal | Deorbited | ||||||||||
| Decay date | October 29, 1966, 13:29:06 UTC[4][2] | ||||||||||
| Orbital parameters | |||||||||||
| Reference system | Selenocentric | ||||||||||
| Semi-major axis | 2,694 km (1,674 mi) | ||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.33 | ||||||||||
| Periselene altitude | 189.1 to 40.5 km (117.5 to 25.2 mi) | ||||||||||
| Aposelene altitude | 1,866.8 km (1,160.0 mi) | ||||||||||
| Inclination | 12 degrees | ||||||||||
| Period | 208.1 minutes | ||||||||||
| Lunar orbiter | |||||||||||
| Orbital insertion | August 14, 1966 | ||||||||||
| Impact site | 6°21′N 160°43′E / 6.35°N 160.72°E | ||||||||||
| Orbits | 577 | ||||||||||
| Transponders | |||||||||||
| Frequency | 2295 MHz[2] | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The 1966 Lunar Orbiter 1 robotic spacecraft mission, part of NASA's Lunar Orbiter program,[9] was the first American spacecraft to orbit the Moon. It was designed primarily to photograph smooth areas of the lunar surface for selection and verification of safe landing sites for the Surveyor and Apollo missions. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data.
Mission summary
[edit]Mission controllers injected the spacecraft into a parking orbit around Earth on August 10, 1966, at 19:31 UTC.[10] The trans-lunar injection burn occurred at 20:04 UTC. The spacecraft experienced a temporary failure of the Canopus star tracker (probably due to stray sunlight) and overheating during its cruise to the Moon. The star tracker problem was resolved by navigating using the Moon as a reference, and the overheating was abated by orienting the spacecraft 36 degrees off-Sun to lower the temperature.[4]
Lunar Orbiter 1 was injected into an elliptical near-equatorial lunar orbit 92.1 hours after launch. The initial orbit was 189.1 km × 1,866.8 km (117.5 mi × 1,160.0 mi) and had a period of 3 hours 37 minutes and an inclination of 12.2 degrees.[10] On August 21, perilune was dropped to 58 km (36 mi) and on August 25 to 40.5 km (25.2 mi). The spacecraft acquired photographic data from August 18 to 29, 1966, and readout occurred through September 14, 1966.
A total of 42 high-resolution and 187 medium-resolution frames were taken and transmitted to Earth covering more than 5 million square kilometers of the Moon's surface, accomplishing about 75% of the intended mission, although a number of the early high-resolution photos showed severe smearing. It also took the first two pictures of Earth from the Moon.[11] Accurate data were acquired from all other experiments throughout the mission.[12]
While not disclosed until after the end of the Cold War, the imaging system on the Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were the same Eastman Kodak cameras developed by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) for the SAMOS reconnaissance satellites.[13] NASA extended the camera innovation further by developing the film onboard the spacecraft and then scanning the photos for transmission via a video signal.[14]
Orbit tracking showed a slight "pear-shape" of the Moon based on the gravity field, and no micrometeorite impacts were detected. The spacecraft was tracked until it impacted the lunar surface on command at 7 degrees north latitude, 161 degrees east longitude (selenographic coordinates) on the Moon's far side on October 29, 1966, on its 577th orbit.[10] The early end of the nominal one-year mission resulted from a shortage of remaining attitude control gas and other deteriorating conditions and was planned to avoid transmission interference with Lunar Orbiter 2.[10]
| Lunar Photographic Studies | Evaluation of Apollo and Surveyor landing sites |
|---|---|
| Meteoroid Detectors | Detection of micrometeoroids in the lunar environment |
| Caesium Iodide Dosimeters | Radiation environment en route to and near the Moon |
| Selenodesy | Gravitational field and physical properties of the Moon |
-
Launch of Lunar Orbiter 1 from an Atlas-Agena rocket in August 10, 1966
-
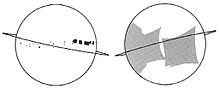
The first image of Earth from the distance of the Moon, August 23, 1966. This probe took a second such image on August 25.
-
Part of the photo to the left as reprocessed by LOIRP in 2008.
-
Full reprocessed image from 2008.
See also
[edit]- Lunar Orbiter Image Recovery Project
- Exploration of the Moon
- List of artificial objects on the Moon
- List of missions to the Moon
References
[edit]- ^ Asif Siddiqi (2018). Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration, 1958–2016 (PDF) (second ed.). NASA. ISBN 978-1-626-83043-1.
- ^ a b c d "Lunar Orbiter 1". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ Lunar Orbiter I: Extended Mission Spacecraft Subsystem Performance (Report). NASA. September 1967. p. 37. NASA-CR-870.
- ^ a b "Lunar Orbiter 1: America's First Lunar Satellite". Drew Ex Machina. 14 August 2016. Retrieved 13 November 2022.
- ^ "Lunar Orbiter 1: Cesium Iodide Dosimeters". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ "Lunar Orbiter 1: Lunar Photographic Studies". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ "Lunar Orbiter 1: Meteoroid Detectors". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ "Lunar Orbiter 1: Selenodesy". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- ^ B. A. Byers (1976). Destination Moon: A History of the Lunar Orbiter Program. NASA. ISBN 978-1-495-92029-5. NASA-TM-X-3487. Retrieved 12 November 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Lunar Orbiter 1". science.nasa.gov. NASA. 12 September 2019. Retrieved 13 November 2022.
- ^ "Lunar Orbiter Photo Gallery - Mission 1". Lunar and Planetary Institute. Retrieved 13 November 2022.
- ^ Thomas P. Hansen (1970). Guide to Lunar Orbiter Photographs. NASA. ASIN B003Z5I8CO. ISBN 978-1-499-16108-3. NASA-SP-242. Retrieved 13 November 2022.
- ^ R. Cargill Hall (October 2001). "SAMOS to the Moon: The Clandestine Transfer of Reconnaissance Technology Between Government Agencies" (PDF). www.nro.gov. National Reconnaissance Office. Retrieved 13 November 2022.
- ^ Jon Kelvey (10 August 2021). "Lunar Orbiter 1: One "Ingenious" Invention Changed Space Exploration Forever". Inverse.com. Retrieved 13 November 2022.





